

We consider volcanoes, types of eruptions, and typical rocks found there. We will emphasize that plate tectonics-the grand unifying theory of geology-explains how the map of our planet's surface has changed radically over geologic time, and why present-day geologic activity-including a variety of devastating natural disasters such as earthquakes-occur where they do. We begin with earthquakes-what they are, what causes them, what effects they have, and what we can do about them. Planet Earth presents an overview of several aspects of our home, from a geological perspective. The boundary along the northern coast of California is a subduction boundary. A well-known example of a transform plate boundary is the San Andreas Fault in California.Earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building, ice ages, landslides, floods, life evolution, plate motions-all of these phenomena have interacted over the vast expanses of deep time to sculpt the dynamic planet that we live on today. Answer (1 of 3): As the San Andreas fault moves off shore north of San Francisco it turns into the Mendocino Fracture zone, trending more east west. Places where these breaks occur are called faults. As the plates rub against each other, huge stresses can cause portions of the rock to break, resulting in earthquakes. This is known as a transform plate boundary. The third type of plate boundary occurs where tectonic plates slide horizontally past each other. While the process of forming these mountain ranges is volcanic, volcanoes and earthquakes along oceanic spreading ridges are not as violent as they are at convergent plate boundaries. Most divergent plate boundaries are underwater and form submarine mountain ranges called oceanic spreading ridges. Along these boundaries, magma rises from deep within the Earth and erupts to form new crust on the lithosphere. When two plates are moving away from each other, we call this a divergent plate boundary. The new magma (molten rock) rises and may erupt violently to form volcanoes, often building arcs of islands along the convergent boundary. As the sinking plate moves deeper into the mantle, fluids are released from the rock causing the overlying mantle to partially melt. Deep trenches are features often formed where tectonic plates are being subducted and earthquakes are common.
Usually, one of the converging plates will move beneath the other, a process known as subduction. If two tectonic plates collide, they form a convergent plate boundary. When two tectonic plates meet, we get a “plate boundary.” There are three major types of plate boundaries, each associated with the formation of a variety of geologic features. San Andreas Fault (Tectonic Evolution (Early transform faulting (Formed: San Andreas Fault (Tectonic Evolution, PlateTectonic Context, Geometry, Modern SAF, Boundary btwn Pac & N.

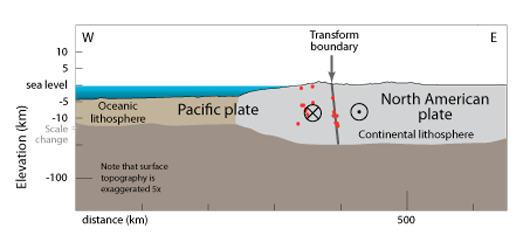
But communities like Desert Hot Springs, San Bernardino, Wrightwood, Palmdale, Gorman, Frazier Park. This forms a transverse fault in stead of the subduction zone usually found where an Ocean Plate and a Continatial plate meet. The two plates hit an angle in California. If you were to stand on the fault and look along its length, this is a type of strike-slip fault where the left block moves toward you and the right block. Is the San Andreas Fault a convergent plate boundary The San Andreas Fault is where the Pacific plate collides with the North American plate. The San Andreas Fault is an example of a right lateral fault. Heat within the asthenosphere creates convection currents that cause tectonic plates to move several centimeters per year relative to each other. San Francisco’s legendary 1906 earthquake, the San Andreas Fault does not go through the city. A fault on which the two blocks slide past one another.
WHAT TYPE OF PLATE BOUNDARY IS THE SAN ANDREAS FAULT SERIES
The Earth’s outer crust (the lithosphere) is composed of a series of tectonic plates that move on a hot flowing mantle layer called the asthenosphere. Can the San Andreas Fault cause a 9.0 earthquake The San Andreas fault is not long and deep enough to have a. This photo shows an explosion near the summit of the West Mata volcano within the Pacific Ocean the image area is about 1.8 meters (6 feet) across in an eruptive zone about the length of a football field that runs along the summit. Is the San Andreas Fault a transform boundary The San Andreas Fault is the transform plate boundary where a thin sliver of western California, as part of the Pacific Plate, slides north-northwestward past the rest of North America. Volcanoes are one kind of feature that forms along convergent plate boundaries, where two tectonic plates collide and one moves beneath the other.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
